Hi, I'm Jovan Espinosa
I am a Data Scientist in career transition, trained at TripleTen LatAm, with a strong professional background in customer service, insurance operations, quality assurance and team training.My previous experience has strengthened key skills – Clear communication, process analysis, leadership, and problem solving – which I now apply to data analysis and predictive modeling.
During my training, I developed projects involving predictive and prescriptive modeling, classification, customer churn prediction, exploration data analysis, and visualization using Python, SQL, Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-Learn, Matplotlib, Seaborn, LightGBM, XGBoost, and Keras.
I have experience with EDA, data Wangling, model evaluation, optimization, and data storytelling.
SKILLS
Technical Skills>Python
>SQL
>Power BI
>Excel
>Git & GitHub
Data Science>Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
>Hypothesis Testing & Applied Statistics
>Customer Segmentation & Clustering
>Prediction with Basic Machine Learning Models
>Cohort Analysis & Customer Retention
>Data-Driven Process Optimization
>A/B Testing & Conversion Analysis
Communication>Data Storytelling
>Effective Communication of Results
>Business-Oriented Visualization
>Designing Narratives for Non-Technical Audiences
>Audiovisual Production Applied to Data Presentation
>Teamwork & Project Leadership
Projects
Project Title
Sentiment Analysis on IMDB Review
This project focuses on binary sentiment analysis of movie reviews from the IMDb dataset.
The goal is to classify reviews as positive or negative using multiple Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques and machine learning models, and to compare their performance.The project was developed as part of a Data Science bootcamp, following a structured end-to-end machine learning workflow.
key features
Models were evaluated using the following metrics:> Accuracy> F1-score> Average Precision Score (APS)> ROC AUC> The F1-score was used as the primary metric for model comparison.Key Findings> Linear models with TF-IDF performed exceptionally well for sentiment classification.> spaCy-based preprocessing slightly improved performance compared to NLTK in Logistic Regression.> Tree-based models (LightGBM, XGBoost) achieved strong results but did not outperform linear models.> Transformer embeddings provided competitive performance but were computationally expensive on CPU.> The Dummy Classifier confirmed that all trained models significantly outperform random guessing.
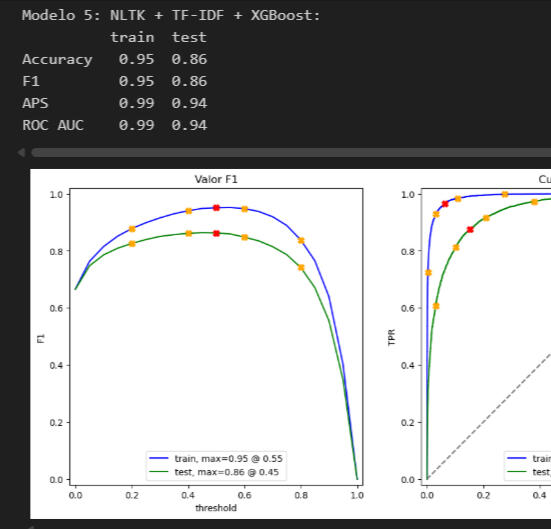
ConclusionThe best-performing models are:> spaCy + Logistic Regression (F1 = 0.90) – Best overall performance> NLTK + Logistic Regression (F1 = 0.89) – Very strong performance> LinearSVC (F1 = 0.88) – Acceptable performanceDifferences in Model Predictions> LinearSVC is more conservative, predicting 2 positive reviews out of 8.> Logistic Regression is more balanced, predicting 4 positive and 4 negative reviews.> Tree-based models tend to be overly optimistic, predicting 6 to 7 positive reviews.This behavior is explained by the fact that LightGBM and XGBoost are more sensitive to specific patterns and may overfit, especially when applied to high-dimensional TF-IDF features.> Linear Models vs Tree-Based Models> Linear models consistently outperform tree-based models:> spaCy + Logistic Regression (0.90) outperforms spaCy + LightGBM (0.87)> NLTK + Logistic Regression (0.89) outperforms NLTK + XGBoost (0.86)Final ConclusionBased on the results, linear models are the preferred choice, especially spaCy + Logistic Regression, because:The F1-score exceeds the required threshold of 0.85It achieves a strong balance between precision and recallThe model is interpretable, as feature importance can be analyzed through coefficientsIt is computationally efficient and suitable for production environments
Tech Stak
| Python | Pandas | NumPy | Scikit-learn | NLTK | spaCy | LightGBM | XGBoost | Hugging Face | Transformers | Jupyter Notebook |
PROJECT TITLE
Telecom Customer Retention
This project aims to predict customer churn (cancellation) for the telecom company Interconnect.
By identifying customers at risk of leaving, the marketing team can offer promotions and special plans to improve retention.
Project workflow
1. Data Preparation & Cleaning
> Merging datasets, handling missing values, feature engineering.2. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
> Understanding churn patterns, class balance check, correlation, visualizations.3. Modeling
> Training baseline and ML models (Dummy, Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting).4. Evaluation
> Comparing models using F1-score (≥0.75 target), ROC-AUC, accuracy, recall.
> Monitoring overfitting (train vs. test performance).5. Insights & Recommendations
> Highlighting key churn drivers and next steps for retention strategy.
Key Features
> Focused on binary classification (Churn: Yes/No).
> Handles class imbalance with resampling techniques.
> Uses baseline model (DummyClassifier) for sanity check.
> Provides visualizations and insights for business decisions.
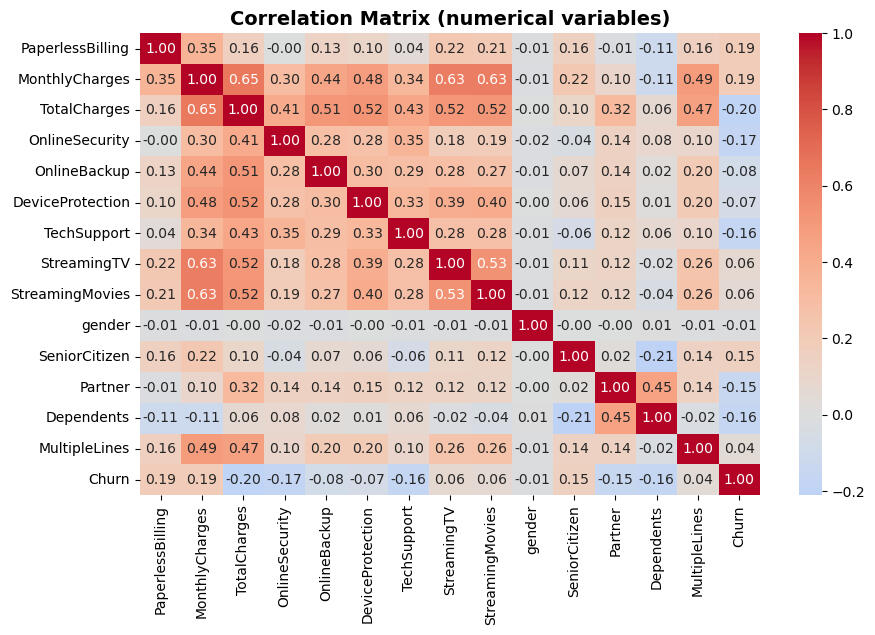
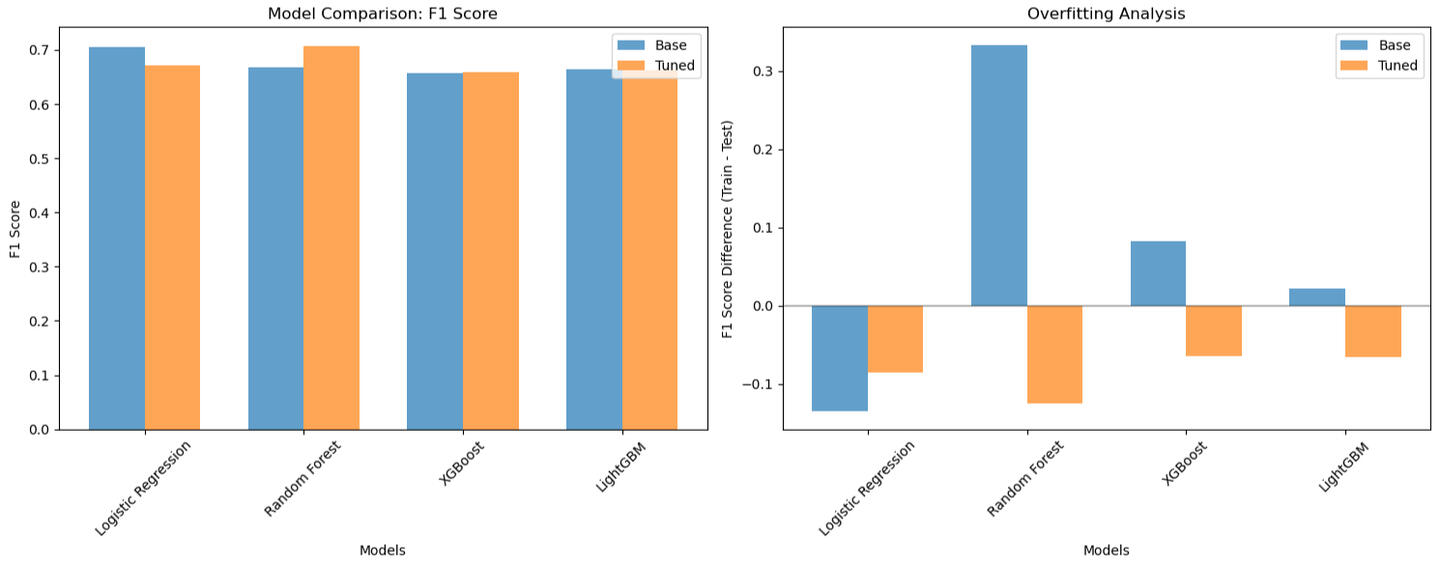
Conculsion
Baseline with DummyClassifier.
> Best-performing model achieved F1-score ≥ 0.75 on test set.
> Insights on key churn factors (e.g., contract type, tenure, payment method).BEST MODEL: Random Forest
Best F1 Score: 0.7068
Best ROC-AUC: 0.7565Result 1 demostrates that through a systematic training evaluation and tuning process, a Random Fores model was identified that achives an optimal balance between detecting the majority of real churns (89.4%), while maintaining acceptable accuracy (58.4%) to optomize marketing resurces.The F1-Score of 0.7068 and ROC-AUC of 0.7565 represent a solid and reliable performance to implement in a production churn prediction system.
Stack
| Pandas | NumPy | Matplotlib | Seaborn | Scikit-learn | XGBoost | LightGMB | Graphviz |
PROJECT TITLE
Used Car Price Estimatior
The project compares multiple regression models — including linear regression, decision trees, random forests, and gradient boosting methods (CatBoost, LightGBM, and optionally XGBoost). Key factors considered are model accuracy (using RMSE), prediction speed, and training time. The ultimate goal is to deliver a reliable, fast, and efficient pricing model for Rusty Bargain's digital platform.Rusty Bargain is a used car sales service developing an app to attract new customers. The app allows users to quickly find the market value of their car and access information such as history, technical specifications, trim versions, and prices.The goal of this project is to build a Machine Learning model that predicts the market value of a car with the highest possible accuracy while keeping prediction and training times efficient.
Project Workflow
Data Load and analyze
> Load dataframe
> Analyze data information and sample rows
EDA
> Modify datatypes
> Handle Null Values
> Feature Engineering
Data preparation for modeling
> Separate features and target
> Train test division
> Use One-Hot Encoding for categorical variablesModel Analysis
Encoding categorical variables according to the model (OHE, LightGBM/CatBoost native encoding).> Model training:
> Linear Regression (baseline)
> Decision Tree
> Random Forest
> LightGBM (Gradient Boosting)
> CatBoost (optional)Evaluation using RMSE, training time, and prediction time measurement.
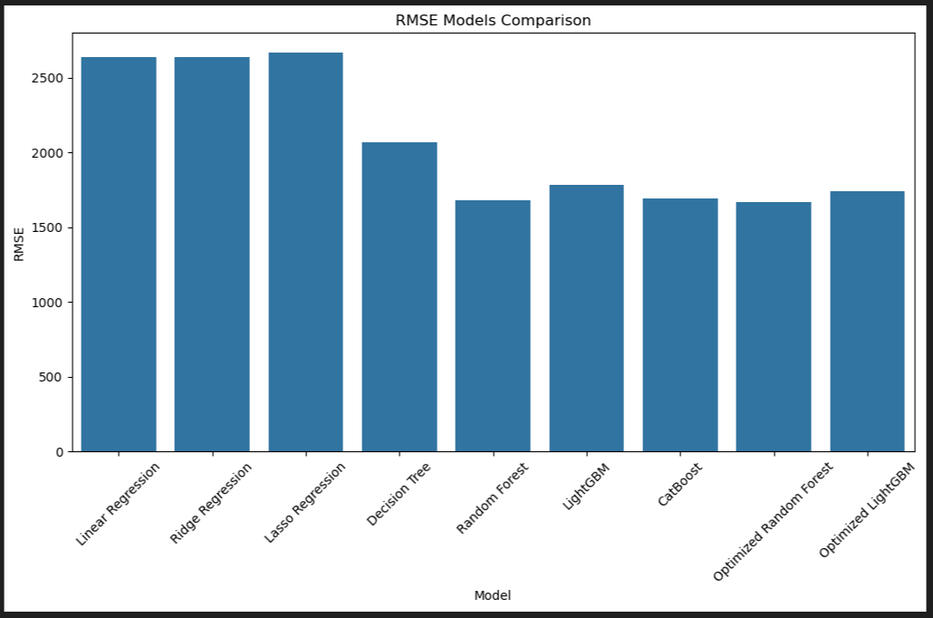
Conclusion
Optimized Random Forest achieved the lowest RMSE, indicating the highest accuracy.Optimized LightGBM had a good balance between accuracy and training speed.Linear models were used as a baseline to validate improvements.Tree-based models showed lower error compared to linear models.Linear regression was used as a reference. LightGBM and CatBoost handle categorical variables natively, while XGBoost requires OHE. Limited hyperparameter tuning was prioritized to save time.Model RMSE (€) / Training Time (s) / Prediction Time (s)Linear Regression 2638.13 24.28 0.57
Ridge Regression 2637.90 4.48 0.80
Lasso Regression 2666.56 902.60 0.60
Decision Tree 2068.40 10.87 0.21
Random Forest 1678.38 383.22 5.15
LightGBM 1782.07 29.27 0.55
CatBoost 1695.03 50.93 0.30
Optimized Random Forest 1666.42 394.48 3.89
Optimized LightGBM 1740.05 20.02 2.25If ultra-fast predictions are the priority, CatBoost or Decision Tree are the winners. Random Forest may be too slow for real-time predictions at high volumes.Training Time
Meaning: Time the model needs to learn from the data. This affects how long it will take to update with new data.Interpretation:Fastest to train: Ridge Regression (4.48s) and Decision Tree (10.87s).Slowest: Lasso (902.6s) and Random Forest (~383–394s).Balanced: CatBoost (50.93s) and Optimized LightGBM (20.02s).If training is frequent, Optimized LightGBM is a great option for its balance of speed and accuracy.If training is occasional and maximum accuracy is the priority, Optimized Random Forest is better, though slower.Final Recommendation:If Rusty Bargain wants maximum accuracy and doesn’t mind slow training → Optimized Random Forest.If prediction speed and solid performance are required → CatBoost.If a balance between fast training and good accuracy is needed → Optimized LightGBM.
Stack
| Pandas | NumPy | Scikit-learn | LightGBM | CatBoost | XGBoost (optional) | Jupyter Notebook |